Product Description
1.Can you provide sample free?
Yes ,we can provide free samples with in 0.5kg.
2.What kind of payment terms you can accept?
We can accept T/T,L/C, Western Union and Paypal.
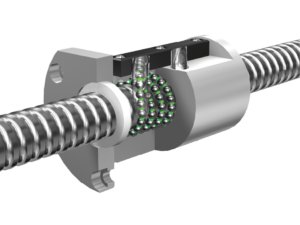
3.What about your steel ball’s quality?
Checking in the whole manufacturing process &100% inspection before shipment ensure the quality of our products.
4.What’s your packing method?
A) Inner packing: Dry packing or oil packing are provided according to you needs.
B) Outer packing:
1)volatile rust preventive paper + poly bag + iron drum + wooden / iron pallet.
2)25kg poly bag + carton + wooden pallet or wooden box.
3)customized packing.
5.What’s your delivery time?
Within 3-30 days according to your required size and quantity.
6.Is your steel ball competitive?
Yes, We are steel ball manufacture more than 30+ years.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Customized: | Customized |
|---|---|
| Certification: | ISO, IATF16949 |
| Standard Parts: | Yes |
| Universal: | Yes |
| Type: | Bearing Ball |
| Material: | Chrome Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
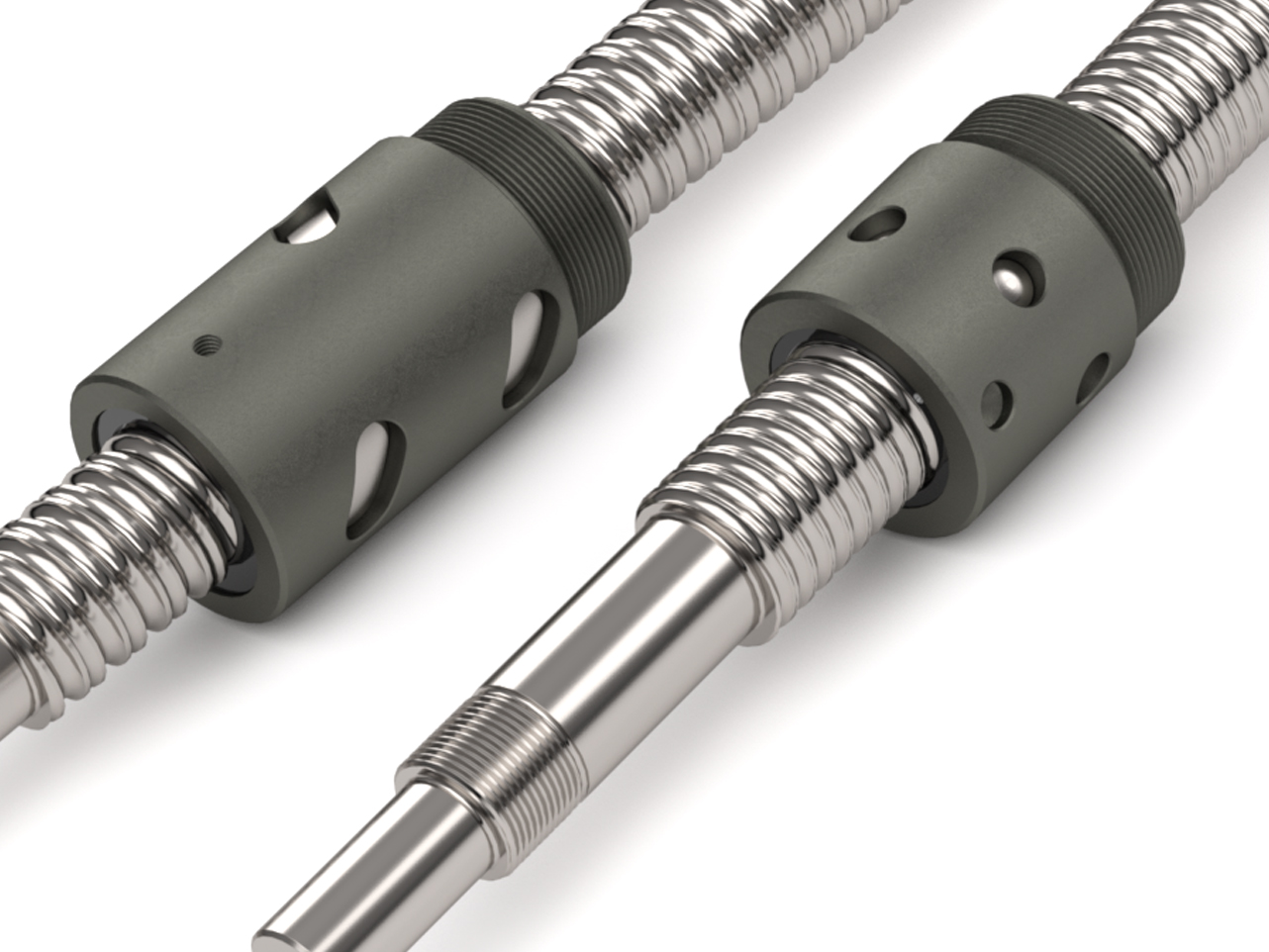

How do screw balls contribute to the efficiency of mechanical systems?
Screw balls, also known as ball screws, play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of mechanical systems. They offer several advantages that contribute to improved performance, reduced energy consumption, and increased overall system efficiency. Here are some key ways in which screw balls contribute to the efficiency of mechanical systems:
- High Efficiency of Power Transmission: Screw balls are highly efficient in converting rotary motion into linear motion. The rolling contact between the ball bearings and the screw threads minimizes friction compared to other types of linear motion systems, such as sliding or belt-driven mechanisms. This high efficiency allows mechanical systems to transmit power more effectively, resulting in reduced energy losses and improved overall efficiency.
- Improved Positioning Accuracy and Repeatability: Screw balls provide excellent positioning accuracy and repeatability, making them ideal for applications that require precise linear motion control. The ball bearings’ rolling contact with the screw threads ensures minimal backlash and hysteresis, resulting in accurate and repeatable positioning. This precision eliminates the need for additional corrective actions, reducing inefficiencies and improving the overall accuracy and efficiency of the mechanical system.
- Reduced Friction and Wear: Screw balls are designed to minimize friction and wear between the ball bearings and the screw threads. The rolling contact reduces sliding friction, resulting in less energy loss due to frictional heating. Additionally, advancements in materials and coatings have further reduced friction and wear, extending the screw ball’s lifespan and reducing the need for frequent maintenance and replacement. The reduced friction and wear contribute to improved efficiency and lower operating costs.
- Increased Load-Carrying Capacity: Screw balls are capable of handling high loads due to their ball bearing design. The load is distributed over a large number of ball bearings, allowing for efficient load transmission and reduced stress on individual components. The ability to handle high loads without sacrificing efficiency makes screw balls suitable for applications that require heavy-duty or high-performance linear motion systems.
- Energy-Saving Features: Manufacturers have introduced energy-saving features in screw ball designs to further enhance efficiency. For example, some screw balls incorporate low-friction ball nuts or optimized ball-to-raceway contact, reducing power requirements. Additionally, advancements in lubrication systems and materials minimize energy losses due to friction, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced operating costs.
- Integration with Automation and Control Systems: Screw balls can be easily integrated with automation and control systems, allowing for precise and efficient motion control. By integrating screw balls with servo motors, drives, and feedback systems, mechanical systems can achieve accurate and synchronized movement, minimizing errors and inefficiencies. This integration enables advanced automation and control strategies, optimizing system performance and energy usage.
By leveraging the advantages of screw balls, mechanical systems can achieve higher efficiency, improved accuracy, and enhanced performance. The reduced friction, high load-carrying capacity, and energy-saving features of screw balls contribute to lower energy consumption, reduced maintenance requirements, and increased productivity. These benefits make screw balls a popular choice in various industries where efficiency and precision are essential, such as robotics, CNC machines, aerospace, and automotive manufacturing.
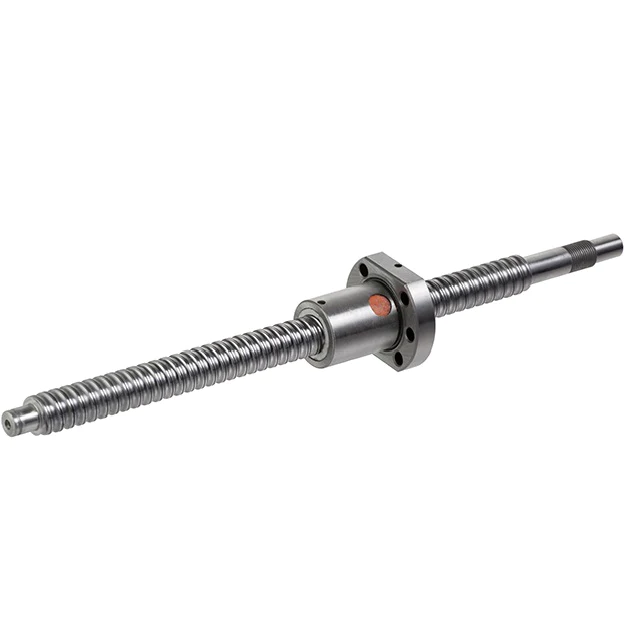

What are the advantages of using a screw ball in mechanical assemblies?
Using a screw ball, also known as a ball screw, in mechanical assemblies offers several advantages over other types of linear motion systems. These advantages make screw balls a popular choice in various applications that require precise and efficient linear motion. Here are some key advantages of using a screw ball:
- High Efficiency: Screw balls are designed for high efficiency in converting rotational motion into linear motion. The rolling contact between the ball bearings and the raceway reduces frictional losses, resulting in improved power transmission and energy efficiency compared to systems with sliding friction.
- Precision and Accuracy: Screw balls provide high levels of precision and accuracy in linear motion. The combination of a specialized thread configuration and ball bearings minimizes axial play and backlash, resulting in precise positioning and repeatability. This makes screw balls ideal for applications that require accurate and reliable motion control.
- Load-Carrying Capacity: Screw balls are designed to handle higher loads compared to other linear motion systems. The presence of ball bearings distributes the load evenly along the screw shaft, reducing stress concentrations and allowing for increased load-carrying capability and improved rigidity.
- Longevity and Durability: Screw balls are constructed from materials such as steel or ceramics, chosen for their durability and strength. These materials provide excellent resistance to wear, corrosion, and fatigue, ensuring long service life and reliable performance even in demanding operating conditions.
- Backlash Reduction: Backlash, which refers to the amount of free motion or play between the screw and the nut, is minimized in screw ball systems. This reduction in backlash enhances system responsiveness, eliminates positioning errors, and improves overall accuracy in applications that require precise control.
- High-Speed Capability: Screw balls can operate at high speeds while maintaining accuracy and stability. The rolling contact between the ball bearings and the raceway reduces friction, enabling smooth and efficient motion even at high rotational speeds.
- Low Maintenance: Screw balls require minimal maintenance compared to other types of linear motion systems. Proper lubrication and periodic inspections are typically sufficient to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The reduced maintenance requirements contribute to cost savings and increased uptime in industrial and automation applications.
- Compact Design: Screw balls offer a compact and space-saving design for linear motion applications. The axial arrangement of the screw and ball nut allows for a more compact assembly, making them suitable for installations with limited space constraints.
These advantages make screw balls well-suited for a wide range of applications, including robotics, CNC machinery, semiconductor equipment, aerospace systems, and medical devices, where precise linear motion control and high efficiency are critical.
When considering the use of screw balls in mechanical assemblies, it is essential to evaluate the specific requirements of the application, including load capacity, speed, accuracy, and environmental conditions. Consulting the manufacturer’s documentation, technical specifications, or seeking professional advice can help in determining the suitability of screw balls for a given mechanical assembly.
How do you select the right size of a screw ball for a specific application?
Selecting the right size of a screw ball, or screw, for a specific application involves considering several factors that influence the functionality and performance of the screw. Here are some key considerations when determining the appropriate size:
- Thread Type: The first step in selecting the right screw size is to determine the thread type required for the application. Common thread types include machine screw threads, wood screw threads, self-tapping screw threads, and sheet metal screw threads. Each thread type has specific dimensions and characteristics that influence the choice of screw size.
- Diameter: The diameter of the screw is a critical factor in determining its size. It is typically measured as the major diameter, which is the outside diameter of the threaded portion of the screw. The diameter should match the size of the hole or the material being fastened. Using a screw with the correct diameter ensures proper thread engagement and adequate holding strength.
- Length: The length of the screw is determined by the thickness of the materials being joined. The screw should be long enough to penetrate through the first material and provide sufficient engagement in the second material to create a secure connection. It is important to consider the total thickness of the materials and any additional components, such as washers or spacers, when determining the appropriate screw length.
- Head Type: The head type of the screw should also be considered for specific applications. Common head types include flat head, pan head, round head, and countersunk head. The choice of head type depends on aesthetic preferences, flushness requirements, and the type of tool used for installation.
- Material: The material of the screw should be selected based on the application’s environmental conditions and the materials being fastened. Different materials offer varying levels of corrosion resistance, strength, and compatibility with specific materials. Common screw materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, and aluminum.
- Load and Application: Consider the anticipated load and the specific application requirements. If the screw will be subjected to heavy loads or vibrations, it may be necessary to choose a larger size or a screw with additional features like locking threads or increased tensile strength.
When selecting the right size of a screw ball, it is essential to consult the manufacturer’s specifications, guidelines, or engineering resources specific to the application. These resources often provide detailed information on recommended screw sizes based on the intended use, material compatibility, and load requirements.
It is also advisable to consult with professionals, such as engineers or experienced tradespeople, who have expertise in the specific application or industry. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on their experience and knowledge of best practices.
By considering factors such as thread type, diameter, length, head type, material, load, and application requirements, the appropriate size of a screw ball can be selected to ensure optimal performance, durability, and reliability in a specific application.


editor by CX 2024-03-04
Leave a Reply